
At the top of the Wireshark window, click on the “Filter” dialog box. Each Wireshark packet contains a protocol, and you can bring it up by using the display filter. Once you’re done, select “Clear” from the toolbar to reconfigure the packet list pane.Ī protocol is a guideline that determines the data transmission between different devices that are connected to the same network. Find the IP address you’re interested in by scrolling through the list. The packet list pane will be reconfigured only to show the packet destination.  Enter “ ip.addr = 8.8.8.8” into the Wireshark “Filter Box.” Then, click “Enter.”. If you want to know the IP address of a particular packet’s destination, you can use the display filter to locate it. Keep in mind the cloning might take a while, especially if you have a sluggish network connection. ”Īll the sources will be subsequently copied to your device. If you don’t have a GitLab account, try the HTTPS URL: “ $ git clone -o upstream. Use the “ $ git clone -o upstream :wireshark/wireshark.git” SSH URL to make the copy. Next, make a clone of the Workshark source. Double-check if your email address and username are configured. Make sure Git is functional by using this command: “ $ git -–version.”. Once you’ve registered an account, follow these steps: It’s possible to do it without one, but it’s better to sign up just in case. However, the method requires you to have a GitLab account.
Enter “ ip.addr = 8.8.8.8” into the Wireshark “Filter Box.” Then, click “Enter.”. If you want to know the IP address of a particular packet’s destination, you can use the display filter to locate it. Keep in mind the cloning might take a while, especially if you have a sluggish network connection. ”Īll the sources will be subsequently copied to your device. If you don’t have a GitLab account, try the HTTPS URL: “ $ git clone -o upstream. Use the “ $ git clone -o upstream :wireshark/wireshark.git” SSH URL to make the copy. Next, make a clone of the Workshark source. Double-check if your email address and username are configured. Make sure Git is functional by using this command: “ $ git -–version.”. Once you’ve registered an account, follow these steps: It’s possible to do it without one, but it’s better to sign up just in case. However, the method requires you to have a GitLab account. Wireshark tutorial sniff network traffic code#
If you want to obtain the source code of a Wireshark repository, you can download it by using a Git client. Apart from the default precision setting, there’s also:Īs the name suggests, the source of the packet is the place of origin. In addition, you can set the preferred precision or number of decimal places that are displayed. You can choose the format in which the timestamps will be displayed in the packet list. That’s why the accuracy of the timestamp can vary from file to file. However, the source of the timestamp is actually the kernel. Instead, the analyzer tool gets them from the Npcap library. Wireshark doesn’t create the timestamps themselves. The timestamps are then included in the packet list pane and available for later inspection. Info: The column includes any additional information about a particular packet.Īs Wireshark analyzes the network traffic, each captured package is time stamped.
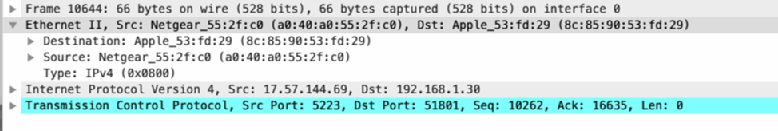
Length: It shows the number of bytes contained in the captured packet.Protocol: It displays the name of the protocol, typically in an abbreviation.Destination: It shows the place where the packet will be kept.Source: It shows where the packet originated.Time: As you might’ve guessed, the packet’s timestamp is displayed here.
The digits will remain the same even after filtrating the data. (Number): As mentioned, you can find the exact number of captured packets in this column. Since the packets are organized in several columns, it’s fairly easy to interpret. The packet list pane will show you the exact number of captured data bits.
Choose the color with which you want to label it. From the list of options, select “Colorize With Filter.”. Right-click on the packet in the packet list pane. However, if you only want to change the coloring rules temporarily, follow these steps: You’ll see the option to customize the colorization to your liking. Choose “Coloring Rules” from the drop-down panel. Select the “View” tab from the toolbar at the top of the screen. Right-click on the packet you wish to examine. Of course, you don’t have to memorize the meaning behind each color. For example, TCP traffic is usually highlighted with blue, while black is used to indicate packets containing errors. Each packet is marked with a different color that represents different types of traffic. As mentioned, Wireshark uses a color-coding system for data visualization.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
